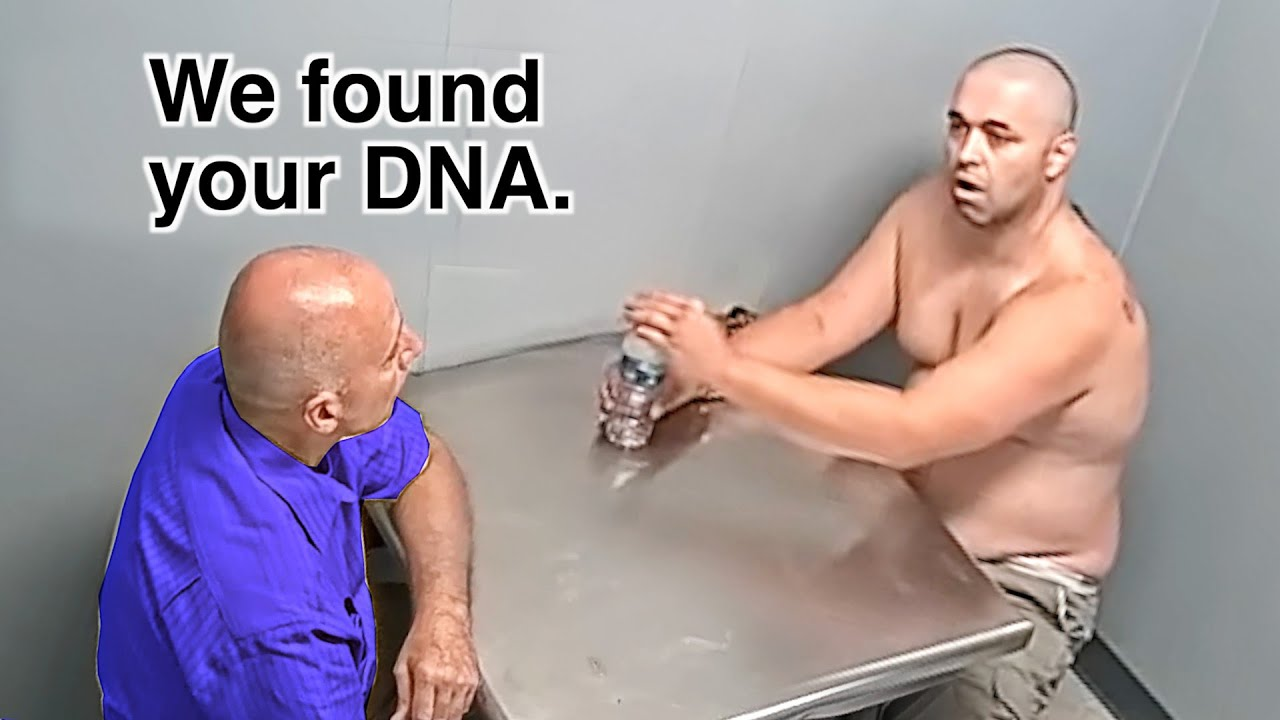
A Complete Timeline of the Idaho Murders Case and Bryan Kohberger’s Guilty Plea
Just weeks before going to trial, the 30-year-old pleaded guilty to killing four college students in November 2022
Getty Images
On November 13, 2022, four University of Idaho students—Kaylee Goncalves, 21; Madison Mogen, 21; Xana Kernodle, 20; and Ethan Chapin, 20—were murdered in an off-campus residence in Moscow, Idaho. Goncalves, Mogen, and Kernodle were roommates, and Chapin, Kernodle’s boyfriend, was staying there on the night of the attack.
For Moscow, which had not seen a murder since 2015, the killings seemed incomprehensible. There were no indications of forced entry into the residence, and authorities didn’t find the murder weapon—believed to be a fixed-blade knife. Police initially stated these were targeted killings but couldn’t name a suspect. Eventually, though, the investigation led to police across the country to primary suspect Bryan Kohberger.
It’s been nearly three years since the 30-year-old was arrested and charged with the gruesome stabbing deaths. His motive is still unknown, and the suspected murder weapon, a KA-BAR knife, hasn’t been recovered.

More From Biography

Kohberger seemed poised to defend his innocence at trial this August, but now the case is nearing an abrupt conclusion in light of Kohberger’s surprising decision to admit to the killings. As part of an agreement with prosecutors, Kohberger officially pleaded guilty on Wednesday and is expected to receive four consecutive life prison sentences for the killings.
Here is a full timeline of the Idaho student murders and significant moments in the case from the earliest days of the investigation to Kohberger’s unexpected eleventh hour plea deal.
- The Idaho Student Murders
- The Search for Bryan Kohberger
- The Charges Against Kohberger
- Preparing for the Death Penalty Case
- Kohberger pleads guilty
The Idaho Student Murders
November 13, 2022: The 4 Idaho students are killed
Around 1:45 a.m., Xana Kernodle and Ethan Chapin return to Kernodle’s home at 1122 King Road. Around 1:56 a.m., a private individual drops Madison Mogen and Kaylee Goncalves off at the King Road house. At approximately 4 a.m., Kernodle receives a DoorDash order. Twelve minutes later, she’s using the TikTok app on her phone.Getty Images
An aerial view of the Moscow, Idaho, home where Kaylee Goncalves, Madison Mogen, Xana Kernodle, and Ethan Chapin were murdered.
Between 4 a.m. and 4:25 a.m., Goncalves and Mogen are killed in a bedroom on the third floor of the house. Kernodle and Chapin are murdered in a bedroom on the second floor. Two other roommates are home but not attacked.
At 11:58 a.m., a 911 call made from the phone of one of the surviving roommates comes in about an unresponsive person at the King Road residence. Responding authorities discover the dead bodies. A knife sheath is found on the bed where Goncalves and Mogen lie.
November 17, 2022: Autopsy results indicate the students were sleeping when they were attacked
The Spokane County Medical Examiner’s Office conducts autopsies on the victims. The Latah County Coroner shares initial information that all four were stabbed multiple times. The coroner stated the victims were likely asleep when they were attacked, though some had defensive wounds. None of the victims show signs of sexual assault.
November 20, 2022: Police publicly clear the unharmed roommates from the suspect list
During a press conference about the investigation, Moscow Police Capt. Roger Lanier mentions the two unharmed roommates—later named as Dylan Mortensen and Bethany Funke—were home at the time of the murders. He says neither is considered a suspect.
According to an affidavit of probable cause released on January 5, 2023, a roommate, identified as D.M., told authorities she woke up in her second-floor bedroom around 4 a.m. on November 13 when she heard noise coming from upstairs. A short time later, she thought she heard Goncalves say, “There’s someone here.” She then heard crying from the direction of Kernodle’s room and heard a male voice say, “It’s okay, I’m going to help you.”
D.M. next opened her door and saw a man dressed in black with a mask over the lower part of his face. She describes him as “5-foot-10-inch or taller, male, not very muscular, but athletically built with bushy eyebrows.” D.M. says she was frozen with shock as this unknown man walked past her toward a sliding glass door at the back of the house. She then closed and locked her bedroom door.
November 25, 2022: Authorities seek a white sedan seen in the area around the time of the murders
Moscow police ask area law enforcement to be on the lookout for a 2011 to 2016 white Hyundai Elantra. This request comes after neighborhood surveillance videos show a white sedan driving by the dead-end street where the victims lived several times between 3:29 a.m. and 4:04 a.m. on November 13. The vehicle was then seen quickly driving out of the area at approximately 4:20 a.m. A forensic examiner identifies the make, model, and possible year of the vehicle.
Keep Reading
The Search for Bryan Kohberger
November 29, 2022: Kohberger becomes a person of interest
Washington State University police inform Moscow police that a 2015 white Hyundai Elantra is registered on their campus. The car is registered to Bryan Kohberger, a 28-year-old Ph.D. student in criminology. Washington State University is in Pullman, Washington, eight miles from Moscow.
Later, a Moscow police officer reviews Kohberger’s Washington state driver’s license photograph. Kohberger’s appearance matches that of the unknown man D.M. saw on November 13.Getty Images
Bryan Kohberger
December 23, 2022: Authorities obtain Kohberger’s cell phone records
Moscow police are granted a warrant to track Kohberger’s cell phone. The phone was in Pullman around 2:47 a.m. on November 13. At the time of the murders, Kohberger’s phone wasn’t connected to any network, which can happen when a phone is turned off or in airplane mode. At approximately 4:48 a.m. on November 13, Kohberger’s phone reconnected to the cell network at a location south of Moscow.
Cell phone records also reveal Kohberger’s phone was close to the crime scene between 9:12 a.m. and 9:21 a.m. on November 13. Historical location data indicates Kohberger’s phone had been near the King Road residence 12 times before November 13. These visits go back to at least August 2022.
December 27, 2022: Kohberger returns to his parents’ Pennsylvania home
Kohberger, who has driven his Elantra to his parents’ home in Albrightsville, Pennsylvania, is under surveillance. Authorities collect trash from the northeastern Pennsylvania home and send the items to Idaho to try to retrieve a DNA sample.
December 28, 2022: DNA links Kohberger to the murders
The Idaho State Lab compares DNA obtained from the trash to DNA found on the knife sheath left at the crime scene. A DNA profile from the Pennsylvania trash shows a near certain probability of a familial match on the sheath through Kohberger’s father. Later samples taken from Kohberger after his apprehension provide a “statistical match.”
December 30, 2022: Police arrest Kohberger in Pennsylvania
In a pre-dawn raid, Kohberger is arrested at his parents’ home in Pennsylvania. He is charged with four counts of first-degree murder and one count of felony burglary.
The Charges Against Kohberger
January 3, 2023: Kohberger agrees to return to Idaho
Kohberger appears in court in Pennsylvania. He agrees to be extradited back to Idaho, where a judge has issued a gag order that bars attorneys and officials from discussing the case with the public.
January 4, 2023: The suspect is booked into Latah County Jail
After arriving in Idaho via plane, Kohberger is booked into Latah County Jail, which is connected to the Latah County Courthouse in Moscow.Getty Images
Bryan Kohberger appears at a hearing in Latah County District Court on January 5, 2023, in Moscow, Idaho.
January 5, 2023: A judge orders Kohberger to be held without bail
Kohberger appears before Latah County Magistrate Judge Megan Marshall, who orders him to be held without bail. He returns to court for a second appearance on January 12 with his lawyer, public defender Anne Taylor.
May 17, 2023: A grand jury charges Kohberger with murder
Prosecutors take the case before a grand jury, forgoing a preliminary hearing. The jury returns an indictment for Kohberger with the same charges as announced in December: four counts of first-degree murder and one count of burglary.
At his ensuing arraignment, Kohberger chooses to stand silent and doesn’t enter a plea, prompting a judge to enter a “not guilty” plea on his behalf.
Dive Deeper
December 28, 2023: The scene of the crime is demolished
The University of Idaho demolishes the off-campus home where the murders took place despite pushback from the families of Goncalves and Kernodle, who argued the residence could be a source of evidence during Kohberger’s trial. “While we appreciate the emotional connection some family members of the victims may have to this house, it is time for its removal and to allow the collective healing of our community to continue,” University of Idaho President Scott Green says.
Preparing for the Death Penalty Case
September 9, 2024: The trial is moved from Moscow to Boise
An Idaho Second District judge approves a change of venue from Moscow to Boise, Idaho, for Kohberger’s trial, citing extensive media coverage of the case and statements from public officials suggesting his guilt that might lead to an unfair trial.
November 20, 2024: A judge allows prosecutors to seek the death penalty
The district court judge overseeing the trial rules that prosecutors can seek the death penalty against Kohberger if he’s convicted. The move rejects the defense’s argument that Idaho’s methods of capital punishment are unconstitutional and keeping Kohberger on death row would be “dehumanizing.”
Related Stories
March 14, 2025: More details emerge about the 911 call
Audio from the 911 call on the day of the killings is released. During the exchange, a caller reports that a 20-year-old woman is passed out and not waking up and that unspecified roommates “saw some man in their house last night.”
April 24, 2025: The judge confirms the death penalty as a possible punishment
Judge Steven Hippler rejects another appeal to remove the death penalty from the case. Kohberger’s legal team had argued that his recent diagnosis of an autism spectrum disorder “reduces his culpability, negates the retributive and deterrent purposes of capital punishment, and exposes him to the unacceptable risk that he will be wrongfully convicted and sentenced to death.”
Kohberger pleads guilty
June 30, 2025: Prosecutors say Kohberger accepted a plea agreement
A letter sent to victims’ families reveals Kohberger has accepted a plea deal that will prevent him from receiving the death penalty in the case. He’s expected to plead guilty to all four counts of first-degree murder as well as one count of burglary at a hearing. Kohberger will also waive his right to appeal if the agreement is confirmed.
July 2, 2025: Kohberger confesses to the Idaho student murders
Kyle Green, Pool//AP
Bryan Kohberger was seemingly calm as he pleaded guilty.
As Judge Steven Hippler reads off the charges, Kohberger pleads guilty to all five counts and is convicted of quadruple murder and burglary. Prosecutors provide more details from the case, revealing Kohberger’s car had been “pretty much disassembled” internally and cleaned before its seizure and that nothing of value was found inside his “spartan” apartment. They also reveal the knife Kohberger used in the murders has yet to be found.
Hippler schedules Kohberger’s sentencing for 11 a.m. ET on July 23. The victims’ families will be allowed to give impact statements at that time. The judge can choose an alternative sentence to the plea agreement, which stipulates four life sentences running consecutively for each murder, but Kohberger can’t petition for such terms.
This psychologist explains why people confess to crimes they didn’t commit
Ingenious experiments have shown how standard police questioning applies psychological pressure
- 13 Jun 2019
- ByDouglas Starr

Share:
At 16, Huwe Burton confessed to killing his mother. He was still in shock from discovering her body when New York City police began to interrogate him. After hours of being threatened and cajoled, he told the police what they wanted to hear. He soon recanted, knowing he was innocent and hoping the justice system would clear him.
Burton was convicted of second-degree murder in 1991 and received a sentence of 15 years to life.
After 20 years in prison, he was released on parole, but he never could shake the stigma of the conviction. Attorneys from several organizations worked for more than a decade to clear him. They produced facts that contradicted the confession and showed evidence of prosecutorial misconduct. But for the Bronx District Attorney’s Office, Burton’s confession outweighed all other evidence; after all, who would admit to a crime they did not commit? Finally, last summer Burton’s attorneys brought in Saul Kassin, a psychologist at the John Jay College of Criminal Justice in New York City who is one of the world’s leading experts on interrogation.
SIGN UP FOR THE AWARD-WINNING SCIENCEADVISER NEWSLETTER
The latest news, commentary, and research, free to your inbox daily
“I went in prepared to make a 15-minute presentation, but the attorneys started asking some really good questions,” Kassin says. “Before you knew it, we had a discussion that lasted almost 2 1/2 hours.”
Kassin explained that false confessions are not rare: More than a quarter of the 365 people exonerated in recent decades by the nonprofit Innocence Project had confessed to their alleged crime. Drawing on more than 30 years of research, Kassin told the legal team how standard interrogation techniques combine psychological pressures and escape hatches that can easily cause an innocent person to confess. He explained how young people are particularly vulnerable to confessing, especially when stressed, tired, or traumatized, as Burton was.

Kassin’s presentation helped open the prosecutors’ eyes to the emerging science of interrogation and false confession. Six months later, on 24 January, Judge Steven Barrett of the Bronx Supreme Court vacated Burton’s 3-decade-old conviction, citing such work as the basis of his decision. “Having Dr. Kassin come in and give a master class on the science of false confessions was a turning point,” says Steven Drizin, co-director of the Center on Wrongful Convictions at Northwestern University in Chicago, Illinois, who led the team that pursued Burton’s exoneration.
Although scores of people have been cleared of false confessions since DNA evidence entered U.S. courtrooms, the Burton case was the first time someone had been exonerated on the basis of the scientific analysis of interrogation. As such, it marks the coming of age of research that is profoundly affecting the justice system. Confessions are being questioned as never before—not just by defense lawyers, but by lawmakers and some police departments, which are reexamining their approach to interrogation.
Kassin is part of a cadre of scientists who have flipped conventional wisdom about confessions—and about the perception of truth. His cleverly designed experiments have probed the psychology that leads to false confessions. In more recent work, he has shown how a confession, true or not, can exert a powerful pull on witnesses and even forensic examiners, shaping the entire trial.
“Saul Kassin is one of the godfathers of the innocence movement,” says Rebecca Brown, policy director of the Innocence Project in New York City. Drizin has his own metaphor: “If there was a Mount Rushmore to the study of false confessions, Dr. Kassin’s face would be on it.”
“Overpowering influences”
Confessions have always been the “gold standard” indicator of guilt, even though some proved spectacularly misleading. For example, a man who had admitted to a murder in 1819 narrowly escaped hanging when his supposed victim was found living in New Jersey. The first scientific red flag came from Hugo Münsterberg, a renowned Harvard University psychologist, who in 1908 warned about “untrue confessions … under the spell of overpowering influences.” But it took several shocking false confession cases in the late 1980s and the introduction of DNA evidence to the justice system for the extent of wrongful convictions to emerge—and with it how often false confessions played a role.
Kassin was not surprised, having spent years studying police interrogation techniques. In person he projects a kind of affable intensity, with piercing brown eyes and a conversational style that lends urgency to even a casual chat. Raised in a working-class neighborhood of New York City, he got his bachelor’s degree at Brooklyn College in New York (tuition: $53 per semester) and his Ph.D. at the University of Connecticut in Storrs, both in psychology. As a postdoc at the University of Kansas in Lawrence, he studied how juries make decisions and was struck by the power of a confession to practically guarantee a guilty verdict.
Saul Kassin is one of the godfathers of the innocence movement.
- Rebecca Brown, Innocence Project
He also began to wonder how often those confessions were genuine, after he learned about the Reid interrogation technique, the near-universal method taught to police. Its training manual—now in its fifth edition—was first published in 1962 by John Reid, a former Chicago detective and lie detector expert, and Northwestern University law professor Fred Inbau. “I was horrified,” Kassin says. “It was just like Milgram’s obedience studies, but worse.”
Stanley Milgram, a psychologist at Yale University and one of Kassin’s heroes, had conducted studies in the 1960s in which subjects were encouraged to give electric shocks to other subjects who were not learning their lessons quickly enough. The volunteers, who didn’t know the shocks they gave were fake, were disturbingly willing to inflict pain when someone in authority told them to.
A Reid interrogation looks different at first. It starts with a behavioral assessment, in which the officer asks questions—some irrelevant and some provocative—while watching for signs of deception, such as looking away, slouching, or crossing the arms. If the suspect is thought to be lying, the investigator moves on to phase two, the formal interrogation. Now, they amp up the questioning—repeatedly accusing the suspect, insisting on hearing details, and ignoring all denials. Meanwhile, the investigator offers sympathy and understanding, minimizing the moral (but not legal) dimension of the crime and easing the path to confession. (Example: “This never would have happened if she didn’t dress so provocatively.”)
That phase, with an authority figure applying psychological pressure, reminded Kassin of Milgram’s infamous experiments. But whereas Milgram got someone to “harm” another person, the Reid technique gets people to harm themselves by admitting guilt. Kassin suspected that the pressure might sometimes lead to false confessions.
To find out, he decided in the early 1990s to model the Reid technique in the lab, with student volunteers. In what Kassin called the computer crash paradigm, he had students take rapid-fire dictation on computers. He warned them that the system had a glitch and that hitting the Alt key would trigger a crash. That part was a fib: The computers were programmed to crash regardless of which keys were hit. The experimenter then accused the students of hitting the Alt key.
At first, none confessed. Then, Kassin added variables based on what he and other researchers had learned about actual police interrogation tactics. Sometimes, for example, police falsely tell a suspect they have witnesses to the crime—causing a suspect to doubt their own version of events. (Under U.S. law, police are permitted to lie.) In one of the most striking examples, Marty Tankleff, a Long Island teenager, came to breakfast one morning in 1988 to find his parents stabbed on the kitchen floor, his mother dying and his father in a coma. Detectives thought Tankleff was not sufficiently grief-stricken, so he became their prime suspect. After hours of getting nowhere, a detective said he had called Tankleff ‘s father at the hospital and that the injured man said Tankleff had committed the crime. (In truth, his father died without regaining consciousness.) Shocked beyond reason, Tankleff confessed. He spent 19 years in prison before a growing body of evidence set him free.
… confessions that look real can actually be false, even if they’re corroborated by informants and forensic science.
- Saul Kassin, John Jay College of Criminal Justice
Kassin could never simulate that kind of trauma in the lab, but he could set up a variation of the computer crash experiment in which a confederate claimed to have seen the student hit the wrong key. Those students confessed at more than double the rate of students paired with witnesses who said they hadn’t seen anything. Under some circumstances, nearly every student facing a false witness confessed.
Some students ended up believing they really had caused the crash, coming up with explanations such as, “I hit the wrong key with the side of my hand.” So deeply had they internalized their guilt that some refused to believe Kassin when he told them the truth.
Another detective told Kassin that during an interrogation, he didn’t actually lie about the evidence in hand, but said he expected new, potentially incriminating evidence to come in. For example, an interrogator might tell a suspect that they were waiting for lab results on DNA from the crime scene. You might think that doing so would get the innocent to deny the crime more vehemently because they expected the results to absolve them. Kassin, however, had interviewed exonerated men who said the prospect of new evidence had a surprising effect. Some confessed just to get out of the stressful situation, figuring that the evidence would later clear them. “They think their innocence is their ticket out of there,” he says.
Kassin and a colleague tested such police “bluffs” in a variation of the computer crash experiment. This time, in addition to accusing the students, the experimenter said that all the keystrokes had been recorded on the server and would soon be examined. The false confession rate soared. Postexperiment questionnaires revealed that many of the bluffed students, like the men Kassin had interviewed, signed a confession to get out of the room and assumed they’d later be cleared. In that sense, Kassin says, belief in one’s innocence and faith in the justice system can themselves be risk factors.
Deception detection
Social scientists worldwide have repeated variations of the computer crash experiments, with similar results. But critics have questioned Kassin’s findings because the “crimes” his subjects were charged with could have been simple acts of carelessness, committed unwittingly, and because confessing bore no serious consequences. Joseph Buckley, president of John E. Reid & Associates Inc. in Chicago, the company that copyrighted the Reid technique in the early 1960s, adds that Kassin’s studies lack validity because they were not conducted using professional interrogators. Buckley says false confessions occur only when interrogators don’t closely follow procedures. In a January report, Buckley said the Reid technique isn’t meant to force a confession. Instead, he wrote, its goal “is to create an environment that makes it easier for a subject to tell the truth.”
Work by other researchers has answered some of those criticisms. Social psychologist Melissa Russano at Roger Williams University in Bristol, Rhode Island, designed an experiment in which volunteers were asked to solve a set of logic problems—some working in groups and some alone. The researchers stipulated that under no circumstances should anyone assist the students working alone. Beforehand, however, a few students were coached to become visibly upset. That prompted some of their classmates to help, in violation of the rules.
In those experiments, the helpers could not have committed the “crime” without knowing, and confessing carried some consequence because cheating violated the college’s honor code. But, just as Kassin found, accusatory questioning often provoked false confessions. Russano also tested another component of standard interrogations—the “minimization” technique that lowers the emotional barrier to confessing. She and colleagues would say things such as, “You probably didn’t realize what a big deal this was.” That technique increased false confession rates by 35%.
Other researchers, including Gísli Guðjónsson, a former Icelandic detective who became an eminent psychologist at King’s College London, have shown how some individuals are especially susceptible to such pressure. Factors such as mental impairment, youth, and substance addiction make people quicker to doubt their own memory and, under pressure, to confess, Guðjónsson found. Law professor Richard Leo of the University of San Francisco in California reported that fewer than 20% of U.S. suspects invoke their Miranda rights against self-incrimination, perhaps hoping to appear cooperative. He and social psychologist Richard Ofshe, then at the University of California, Berkeley, also described “persuaded” confessions in which a suspect, worn down by hours of interrogation, goes into a fugue and begins to believe their own guilt. The problem is especially pronounced among adolescents like Burton, who are both impressionable and cowed by authority.
Much of the Reid technique involves watching for verbal and nonverbal signs of deception, something many police investigators think they are skilled at doing. Kassin put that confidence to the test more than a decade ago. He recruited the best liars he could find—a group of prisoners at a Massachusetts penitentiary. For a small fee he asked half to tell the truth of their crimes on video and the other half to lie, saying they had committed someone else’s crime. He showed the videos to college students and police. Neither group did particularly well at truth detection (the average person is right about half the time), but the students performed better than the police. Yet the police felt more certain about their conclusions. “That’s a bad combination,” Kassin says. “Their training makes them less accurate and more confident at the same time.”
The power of a confession
A poster in Kassin’s office at John Jay College shows 28 faces: men, women, adults, adolescents, white, black, Hispanic. “Look at how many different types of people there are—all of humanity,” Kassin says. “And what they have in common is that they all gave false confessions. There’s no one kind of person who can give a false confession. It can happen to anybody.”
Kassin has helped many of them. Defense lawyers and human rights organizations around the world often call on him to analyze confessions or testify about the nature of interrogation—sometimes as a paid consultant or witness, sometimes pro bono. One face on the poster belongs to Amanda Knox, the U.S. college student studying in Italy who was coerced into confessing to the murder of her roommate. Kassin’s reports to Italian courts were involved in getting her freed. He testified for John Kogut, a Long Island man who after an 18-hour interrogation falsely confessed to raping and murdering a 16-year-old girl. DNA evidence had won Kogut’s release after he spent 18 years in prison, but prosecutors retried him on the basis of the confession. Kassin’s 2005 testimony helped acquit him.

Then there was Barry Laughman, a man with the mental capacity of a 10-year-old, who in 1987 confessed to raping and murdering an elderly neighbor after police falsely told him they found his fingerprints at the scene. After his confession, the police disregarded all other evidence. Neighbors who offered alibis for Laughman were told they must be mistaken. His blood was type B, but the only blood at the crime scene was type A. So the forensic expert proposed a novel theory: that bacterial degradation could have changed the blood type from B to A. Laughman spent 16 years in prison until DNA evidence finally cleared him. (Kassin later testified when Laughman sued the state.)
To Kassin, Laughman’s case showed that confession doesn’t just trump other evidence, but can corrupt it as well. After a confession, alibis are recanted, witnesses change stories, police ignore exculpatory evidence, and forensic scientists reinterpret material. In Huwe Burton’s case, for example, police had caught a neighbor with a history of violence driving the dead mother’s stolen car, but they did not consider him a suspect because Burton had confessed.
The magnitude of the effect emerged in 2012, when Kassin and colleagues published an analysis of 59 false confession cases from the Innocence Project. Forty-nine of those also involved other mistakes, such as eyewitness errors and mistaken forensics—a far higher proportion than in nonconfession cases. In 30 of those cases, the confession was the first piece of evidence collected. In other words, once the police had a confession, all the other evidence lined up to support it. That has an ironic effect: Even when confessions have turned out to be false, appeals courts have ruled that the other evidence is strong enough to support the conviction, Kassin says. “The courts completely missed out that the other evidence was corrupted.”
Other groups have shown experimentally how a narrative can shape forensic evidence. One dramatic example came in 2011, when U.K. psychologist Itiel Dror and U.S. DNA expert Greg Hampikian tested the people you would least expect to be affected by bias—DNA specialists. Dror and Hampikian obtained the printed DNA results from a rape case in which a man was found guilty. The original genetic analysts had been told that police had a suspect in custody; the forensic experts then determined that the suspect’s DNA was part of the crime scene sample. To see whether knowledge of the arrest caused bias, Dror and Hampikian gave the printouts to 17 experts unconnected with the case and told them nothing about the suspect. Only one of them matched the suspect’s DNA to the crime sample. Such findings support the increasingly popular idea that all forensic science should be “blinded”—conducted without any knowledge about the suspects.
Sometimes a confession will override even untainted DNA evidence. In the infamous “Central Park Five” case dramatized in a new Netflix series, five teenagers in 1989 confessed after hours of interrogation to brutally beating and raping a female jogger in New York City. They quickly recanted, and none of the DNA recovered from the victim was theirs. Yet two juries convicted them after the prosecutor explained away the contradiction. She came up with a theory that a sixth unidentified accomplice had also raped the victim and was the only person to ejaculate. (The “unindicted co-ejaculator” theory has been used in other wrongful convictions as well.) Thirteen years later, the man whose DNA matched the sample—a convicted serial rapist and murderer serving a life sentence—confessed that he alone had committed the crime.
How could such an injustice occur? Kassin and a colleague published a study in 2016 in which they simulated the situation with mock jury experiments. When presented with a simple choice between a confession and DNA, people would choose DNA. But if the prosecutor offered a theory as to why the DNA contradicted the confession, the juries overwhelmingly sided with the confession—an insight, he says, into the power of story to influence judgment.
New approaches
Change is coming. By 2010, the evidence about how interrogations can go wrong had become so compelling that Kassin and several colleagues from the United States and United Kingdom wrote an American Psychological Association white paper warning about the risk of coercion. They suggested several reforms, such as prohibiting lying by police, limiting interrogation time, recording all interrogations from start to finish, and eliminating the use of minimization. They also said the practice of seeking confessions was so inherently damaging that it might be necessary to “completely reconceptualize” the tactic and come up with something new.
One model comes from England, where police did away with their Reid-style interrogation system in the early 1990s after several false conviction scandals. Police there now use a system designed to identify deception based not on visible signs of emotional stress, but on “cognitive load,” which can lead liars to stumble as they try to keep their stories straight. English police conduct the kind of open-ended interviews that journalists might use and are encouraged not to go after confessions. Several other countries including New Zealand and Australia, along with parts of Canada, have adopted the new method. They also record the entire interrogation to make the process transparent, something that 25 U.S. states have also adopted.
Two years ago, one of the largest U.S. interrogation trainers, Chicago-based Wicklander-Zulawski & Associates Inc., stopped teaching accusatory interviews and embraced the nonconfrontational methods Kassin and his colleagues advocate. The company was influenced by the proliferation of research and a desire to minimize false confessions, says Dave Thompson, vice president of operations. “We realized there’s a better way to talk to people today than the way we talked to people 20 or 30 years ago.”
Kassin sees progress, too. In March, he spoke to a group that until recently might have been hostile to his message: 40 district attorneys from around the country who want to learn to avoid wrongful convictions. “My point with them was that they are going to be fooled—that confessions that look real can actually be false, even if they’re corroborated by informants and forensic science,” he says. “I wanted to let them know that alarm bells should go off when they see a confession case.”
*Correction, 13 June, 5:25 p.m.: The story has been corrected to indicate that Saul Kassin’s testimony did not secure John Kogut’s exoneration, but helped prevent him from being re-convicted.